Roll grinder
Keywords:
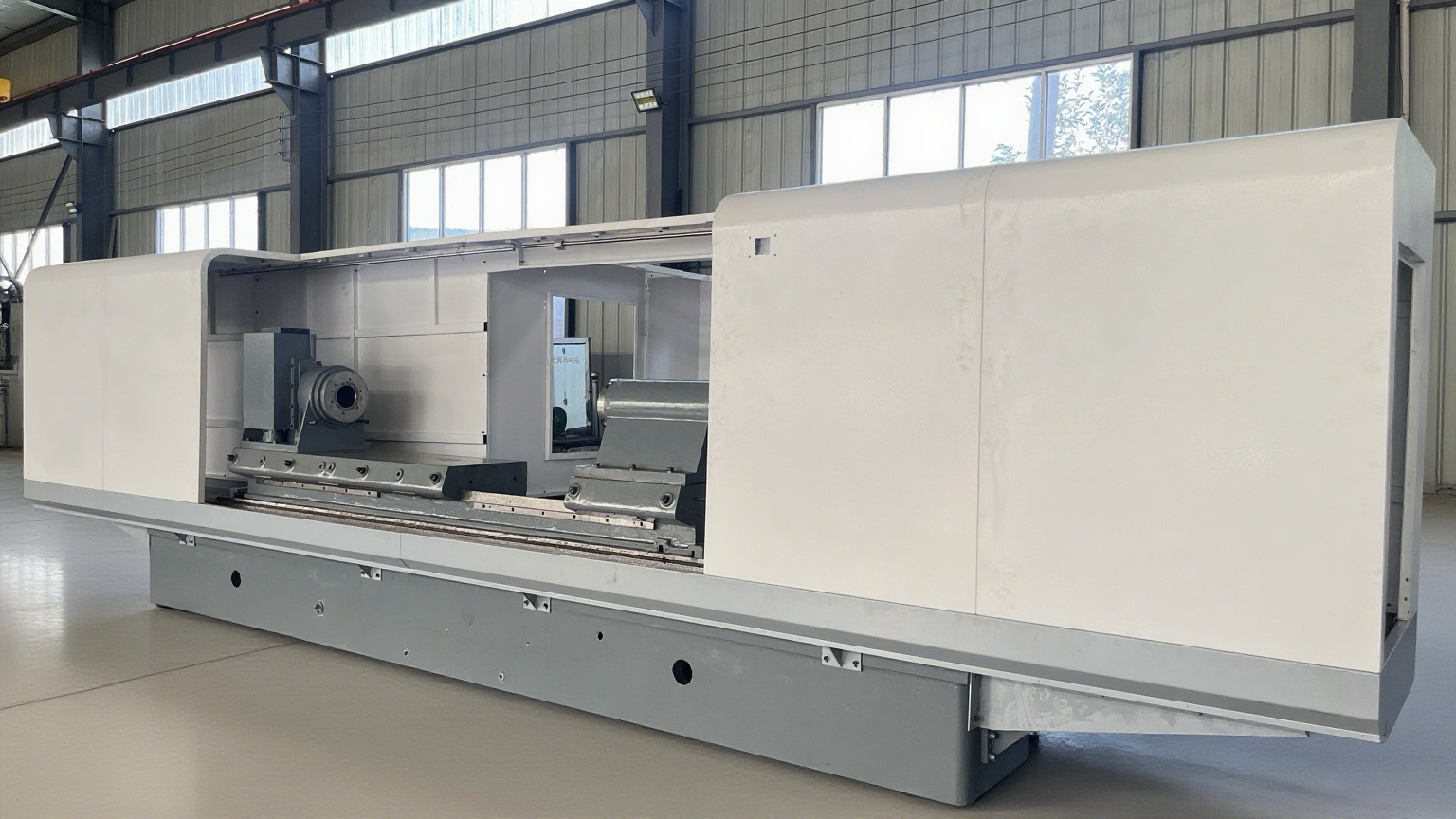
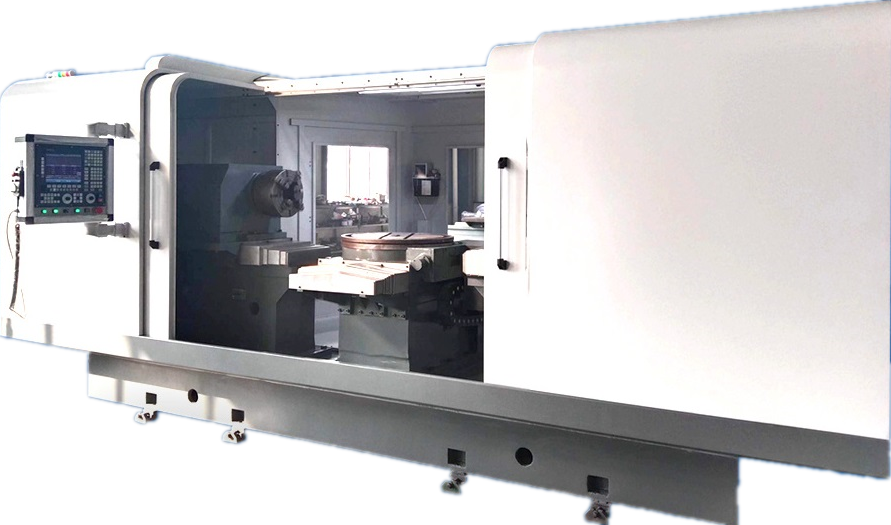
Product Description
Roll grinders are high-precision, specialized grinding equipment used in manufacturing. They primarily grind the rolling surfaces of various workpieces (such as bearings, gears, and cylindrical parts) to achieve ultra-smooth surface quality and strict dimensional tolerances. The following provides a detailed explanation of roll grinders from multiple aspects:
I. Core Features of Roll Grinders
High-precision machining capabilities: Through precise structural design and an advanced control system, it can maintain machining accuracy over time, meeting micron-level or even nanometer-level tolerance requirements.
High-efficiency grinding performance: Combined with suitable grinding wheels and parameter control, it can perform high-efficiency grinding on various materials while ensuring surface finish.
Strong adaptability: Grinding schemes can be adjusted for different workpieces (such as bearing raceways, gear teeth, camshafts, etc.), making it widely applicable.
II. Structure and Design
The structural design of a roll grinder centers around "stability" and "precision," mainly including the following key parts:
1. Bed: Usually cast from cast iron or high-grade steel, providing a rigid base and reducing the impact of vibration on machining accuracy.
2. Guide system: Uses linear roller bearings or hydrostatic bearings to ensure that the workpiece and grinding wheel move smoothly and accurately in the axial and radial directions.
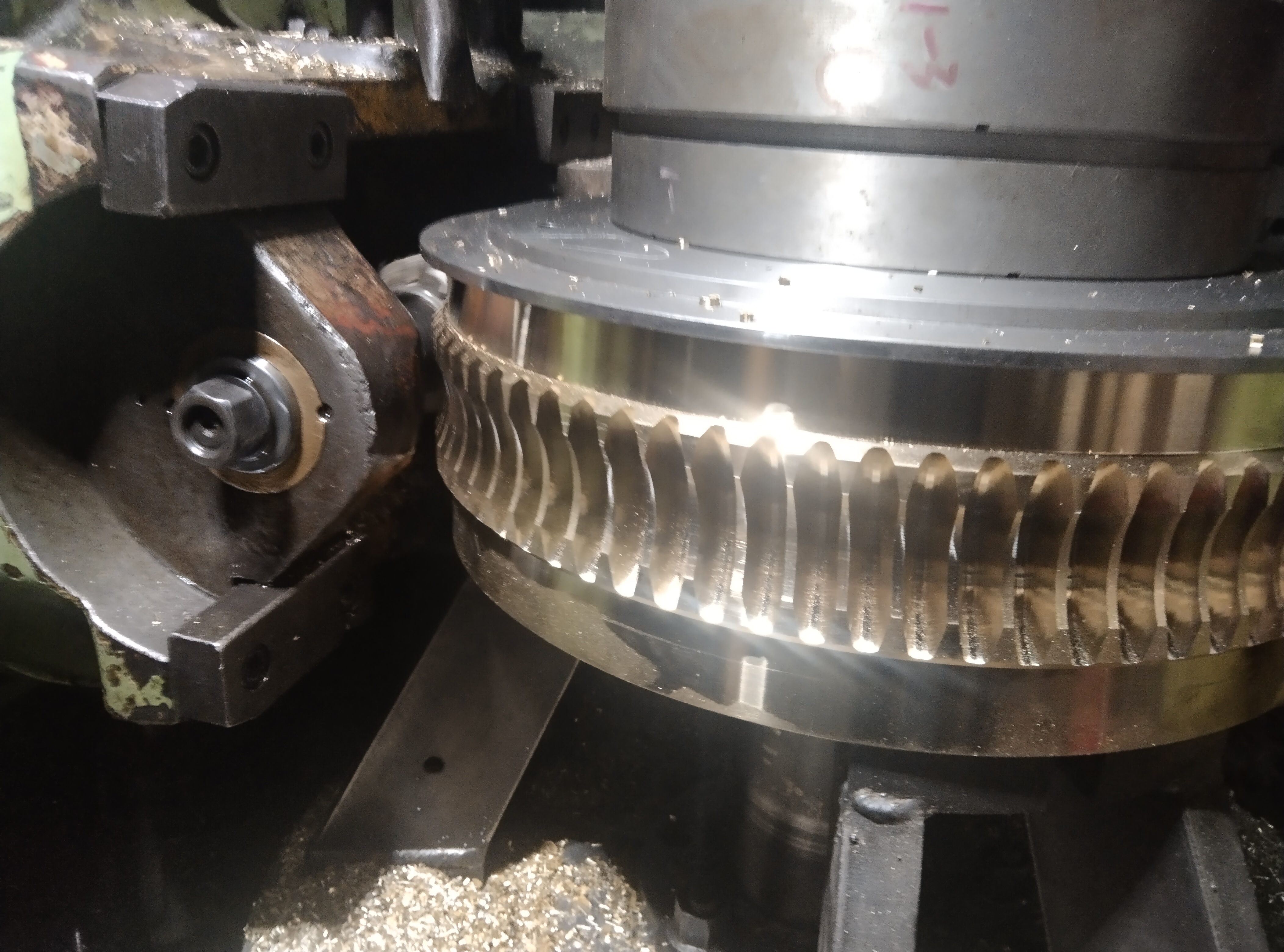
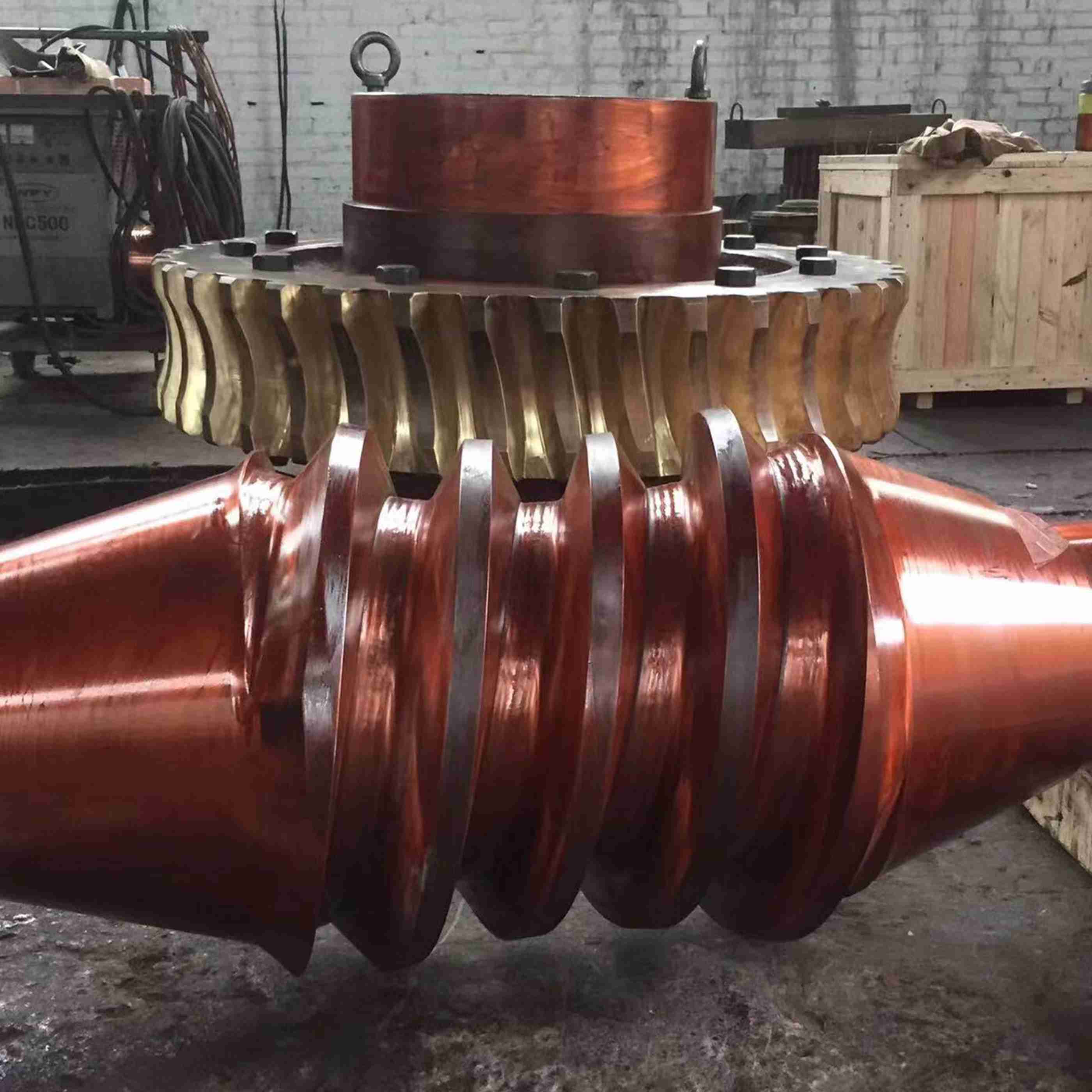
3. Grinding wheel assembly:
Grinding wheel material: Selected according to the workpiece material (e.g., aluminum oxide for steel, silicon carbide for non-metals, cubic boron nitride for ultra-hard materials).
Binding agent: Resin, ceramic, or metal binding agents affect the hardness and self-sharpening of the grinding wheel.
Spindle: Driven by a high-power motor, it rotates at high speed (usually thousands to tens of thousands of revolutions per minute), ensuring grinding efficiency.
4. Automation system:
CNC control system: Programs complex grinding processes to achieve automated processing.
Automatic dressing device: Real-time dressing of the grinding wheel shape and sharpness to maintain grinding accuracy.
Online measurement system: Real-time monitoring of workpiece dimensions, feedback adjustment parameters, and prevents defective products.
III. Working Principle
Roll grinders achieve precise material removal through the "cutting action of abrasive grains." The specific process is as follows:
1. Workpiece clamping: The workpiece is fixed to the worktable or chuck to ensure accurate positioning.
2. Grinding process: The high-speed rotating grinding wheel contacts the slowly feeding workpiece. Through the cutting, scratching, and friction of the abrasive grains, a thin layer of material is removed from the workpiece surface.
3. Cooling system: A large amount of heat is generated during grinding, requiring cooling liquid (such as emulsion, oil-based coolant) to cool the workpiece and prevent thermal deformation or surface burns.
4. Parameter control: The system adjusts parameters such as grinding wheel speed, feed rate, and cutting depth in real-time to ensure that the surface roughness (e.g., Ra 0.01 μm) and dimensional accuracy meet the requirements.
IV. Main Application Areas
Roll grinders are indispensable in industries with stringent precision requirements. Typical applications include:
Automotive industry: Grinding bearing raceways, gear shafts, camshafts, etc., to reduce mechanical friction and improve transmission efficiency.
Aerospace and defense: Machining turbine blades, missile components, etc., to ensure reliability under extreme conditions.
Precision instruments: Manufacturing optical components (such as lens molds), medical implants (such as artificial joints), etc., requiring ultra-smooth surfaces to reduce wear or meet optical performance requirements.
Bearing manufacturing industry: One of the core equipment, used for the final processing of bearing inner and outer ring raceways, directly affecting the service life and rotational accuracy of the bearings.
V. Working Principle
The core of a roll grinder is the removal of material through "controllable abrasive grain cutting action":
1. The workpiece is fed into the grinding area, and the high-speed rotating grinding wheel contacts the workpiece surface, with the abrasive grains removing the surface material.
2. A large amount of heat is generated during grinding, requiring cooling liquid (such as emulsion) to cool the workpiece and prevent annealing or deformation.
3. The CNC system controls parameters such as grinding wheel speed, feed rate, and cutting depth in real-time to ensure processing accuracy.
VI. Technological Development and Trends
Intelligence: Integrating sensors and Internet of Things (IoT) technology to achieve remote monitoring, fault warning, and predictive maintenance, reducing downtime.
New material adaptation: Developing new grinding wheel materials (such as nano-coated grinding wheels) that can efficiently grind difficult-to-machine materials such as ceramics and titanium alloys.
Automation upgrade: Combining robot loading and unloading, online detection and feedback systems to achieve fully unmanned production, improving the consistency of batch processing.
Summary
Roll grinders are key equipment in the high-precision manufacturing field. Through precise structure, automated control, and advanced grinding technology, they provide reliable processing solutions for the bearing, aerospace, automotive, and other industries. With the advancement of intelligent manufacturing, roll grinders are developing towards higher efficiency, greater intelligence, and better adaptability to complex materials, further promoting the precision upgrade of the manufacturing industry.
(See the following figure ↓ )




Classification:
Internal grinder