Herringbone gear
Keywords:
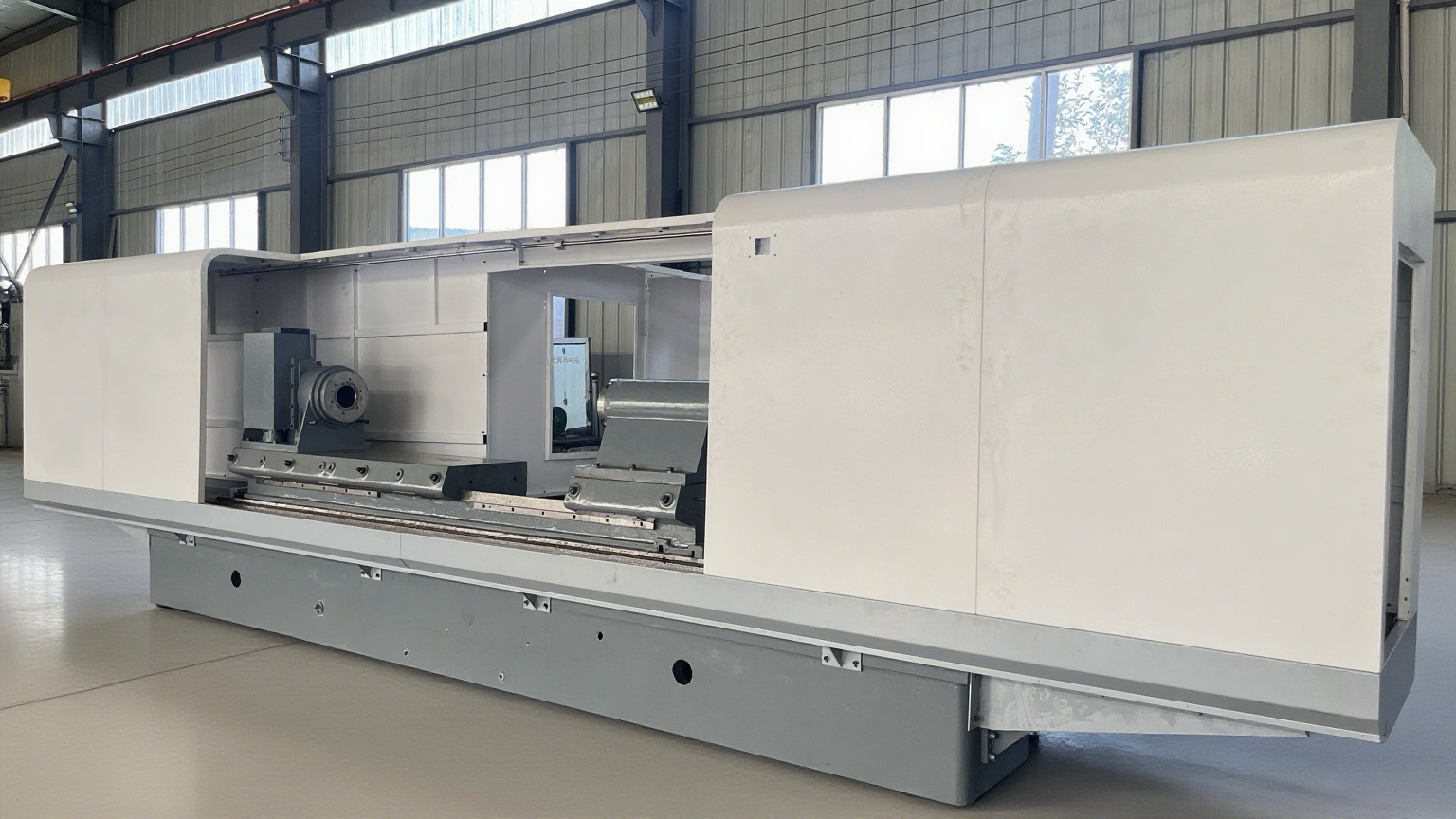
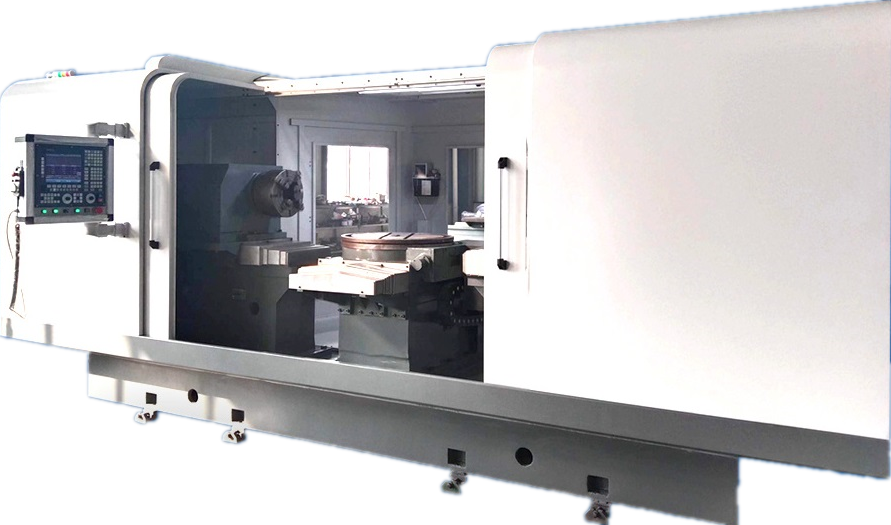
Product Description
Structural Characteristics
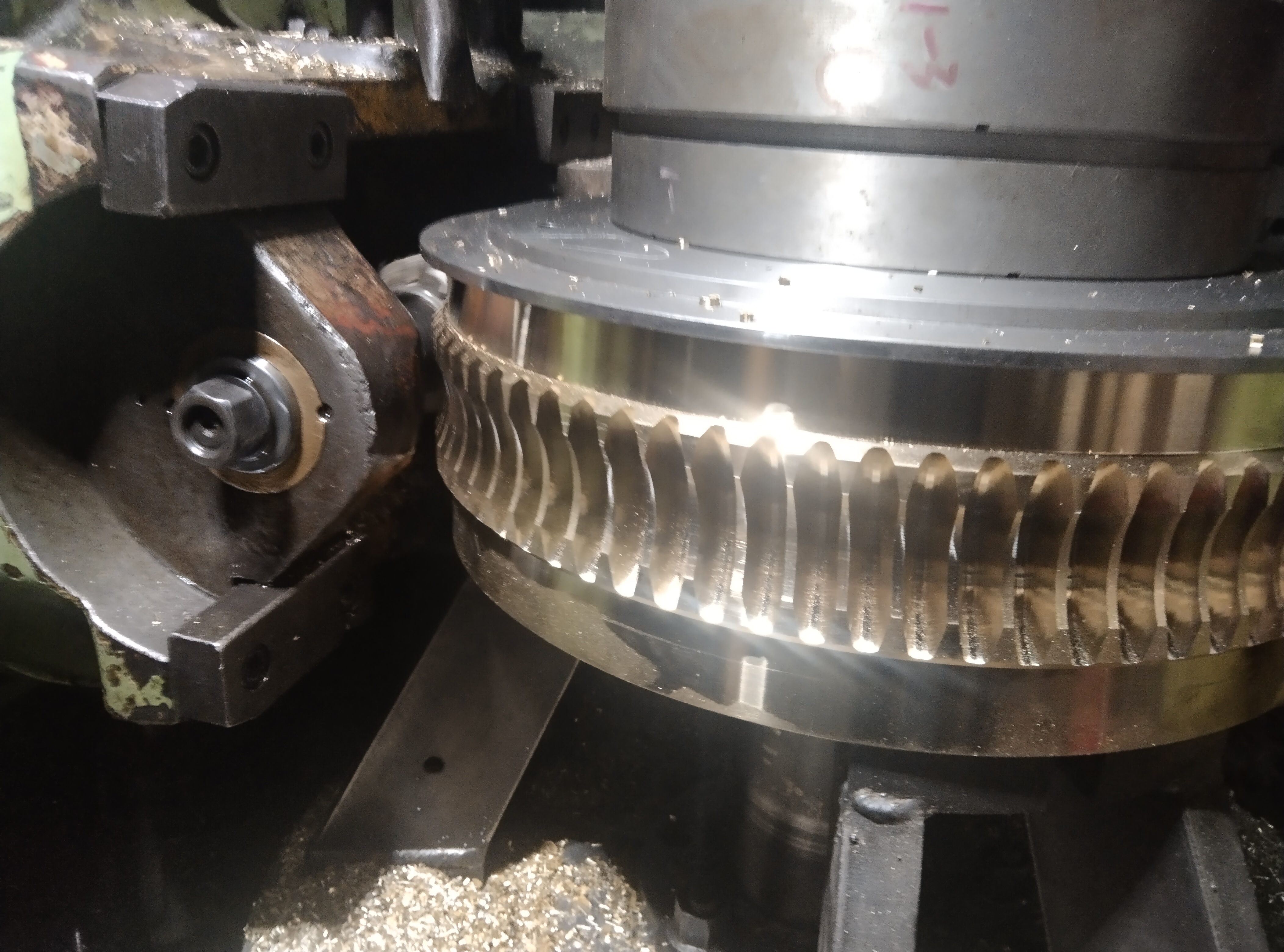
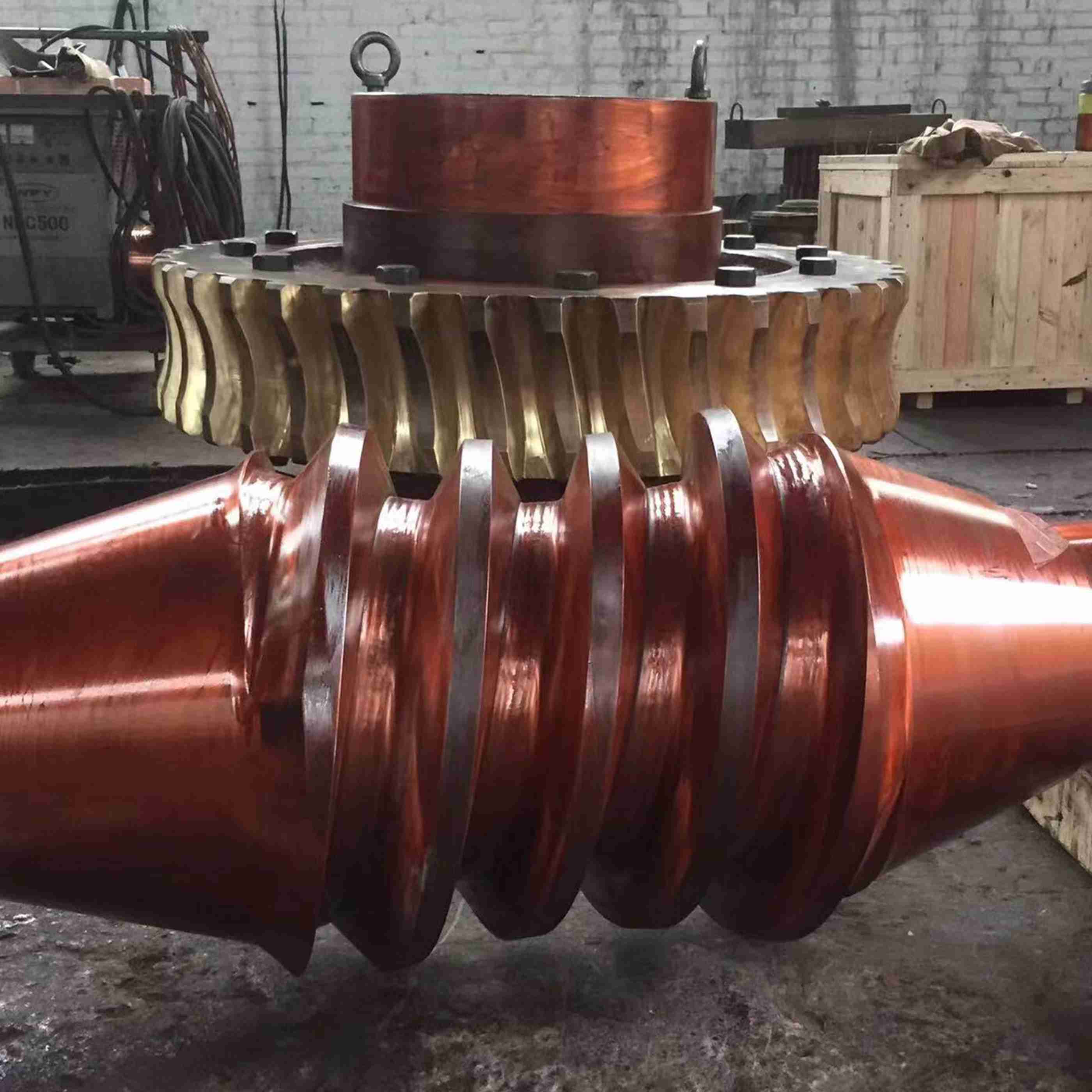
The tooth profile of a herringbone gear is shaped like the Chinese character "人" (rén), which can be seen as a combination of two helical gears with equal but opposite helix angles. The tooth patterns are symmetrically distributed on the left and right sides. This structural design allows the axial forces on both sides of the gear to be balanced during transmission, canceling each other out. Mutual cancellation of axial thrust This eliminates the need for additional thrust bearings to balance axial forces, simplifying the transmission system structure.
Compared to ordinary helical gears, the tooth width (i.e., "length") of herringbone gears can be flexibly customized according to load requirements: In heavy-load scenarios, the tooth width can be increased to expand the contact area and distribute the load; in equipment with space constraints, the tooth width can be shortened to adapt to a compact structure.
Core Performance Advantages
-
Strong Load-Bearing Capacity
The large tooth surface contact area and uniform load distribution allow it to withstand radial forces and torques far exceeding those of spur gears and ordinary helical gears, making it suitable for heavy-duty transmission systems in mining machinery and rolling mills. -
Smooth Transmission, Low Noise
The tooth surface meshing process is a gradual contact, with minimal impact and vibration. It can maintain stability even at high speeds (such as in steam turbines and marine propulsion systems), and the noise is significantly lower than that of spur gears. -
High Efficiency and Long Lifespan
The reasonable tooth profile design reduces friction loss during meshing, with transmission efficiency reaching over 95%. In addition, symmetrical force distribution reduces local wear, resulting in a longer lifespan with regular maintenance.
Typical Application Areas: Heavy machinery, energy equipment, shipbuilding industry, metallurgical equipment
Classification:
Herringbone Gear